4 applications of alginate in the food industry
Introduction
In the dynamically evolving food industry, manufacturers are constantly on the lookout for innovative ingredients that can enhance product quality, shelf life, and consumer appeal. Alginate, a naturally occurring polysaccharide extracted from seaweed, has emerged as a versatile and sought-after ingredient.
1. Alginate Basics: An Overview
Alginate is a hydrocolloid widely used in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. Extracted primarily from brown seaweeds, such as kelp and bladderwrack, alginate possesses unique properties that make it an attractive ingredient for food manufacturers.
2. Classification by Source
Alginate can be classified based on its source, with the two main categories being sodium alginate and calcium alginate. Sodium alginate is derived from brown seaweeds, while calcium alginate is produced by combining sodium alginate with calcium chloride. This classification is vital for food manufacturers to select the appropriate type based on their specific application requirements.
3. Functional Properties
Alginate’s versatile functional properties make it desirable for various food applications. It acts as a thickening agent, stabilizer, emulsifier, and gelling agent. Depending on the desired end-product, food manufacturers can harness alginate’s properties to enhance texture, viscosity, and stability in a wide range of food formulations.
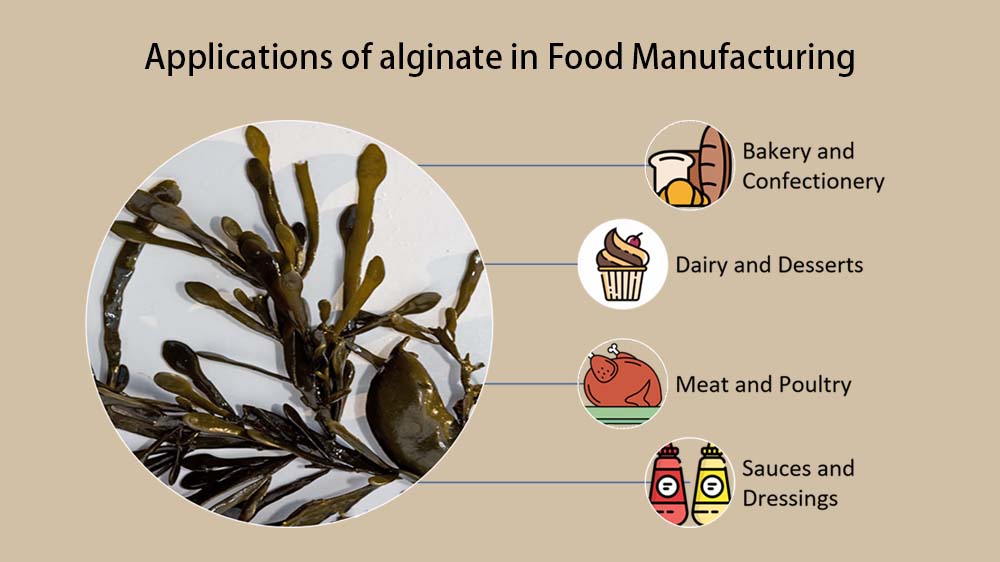
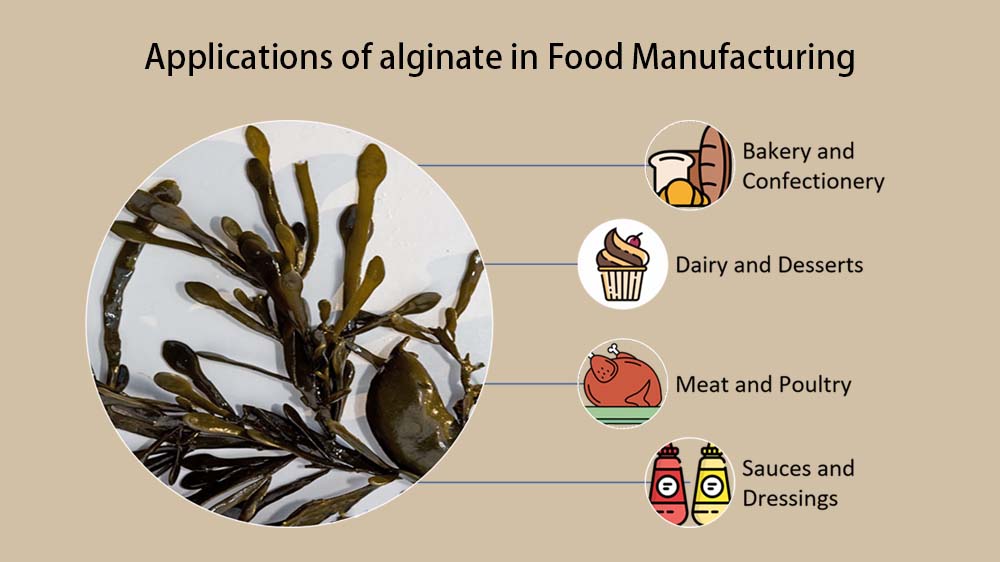
4. Applications in Food Manufacturing
Alginate finds extensive use in the food industry due to its ability to improve product quality and extend shelf life. Some key applications to mention are:
a. Bakery and Confectionery: Alginate can enhance dough stability, improve texture in baked goods, and prevent sugar crystallization in confectionery products.
b. Dairy and Desserts: It can serve as a thickening agent in yogurt, ice cream, and custards, improving texture and providing a creamy mouthfeel.
c. Meat and Poultry: Alginate’s binding properties contribute to improved texture and reduced cooking loss in processed meats, such as sausages and burger patties.
d. Sauces and Dressings: Alginate acts as a stabilizer, preventing phase separation and enhancing the viscosity of sauces and dressings.
5. Health Benefits
Alginate has been associated with various health benefits, such as promoting satiety, reducing calorie absorption, and aiding digestive health.
Conclusion
Alginate’s unique properties and versatile applications make it an indispensable ingredient for food manufacturers.